Landslide Monitor
InSAR-derived deformation maps detect millimeter-scale ground movements over time, enabling proactive landslide risk assessment and early warning for vulnerable slopes.
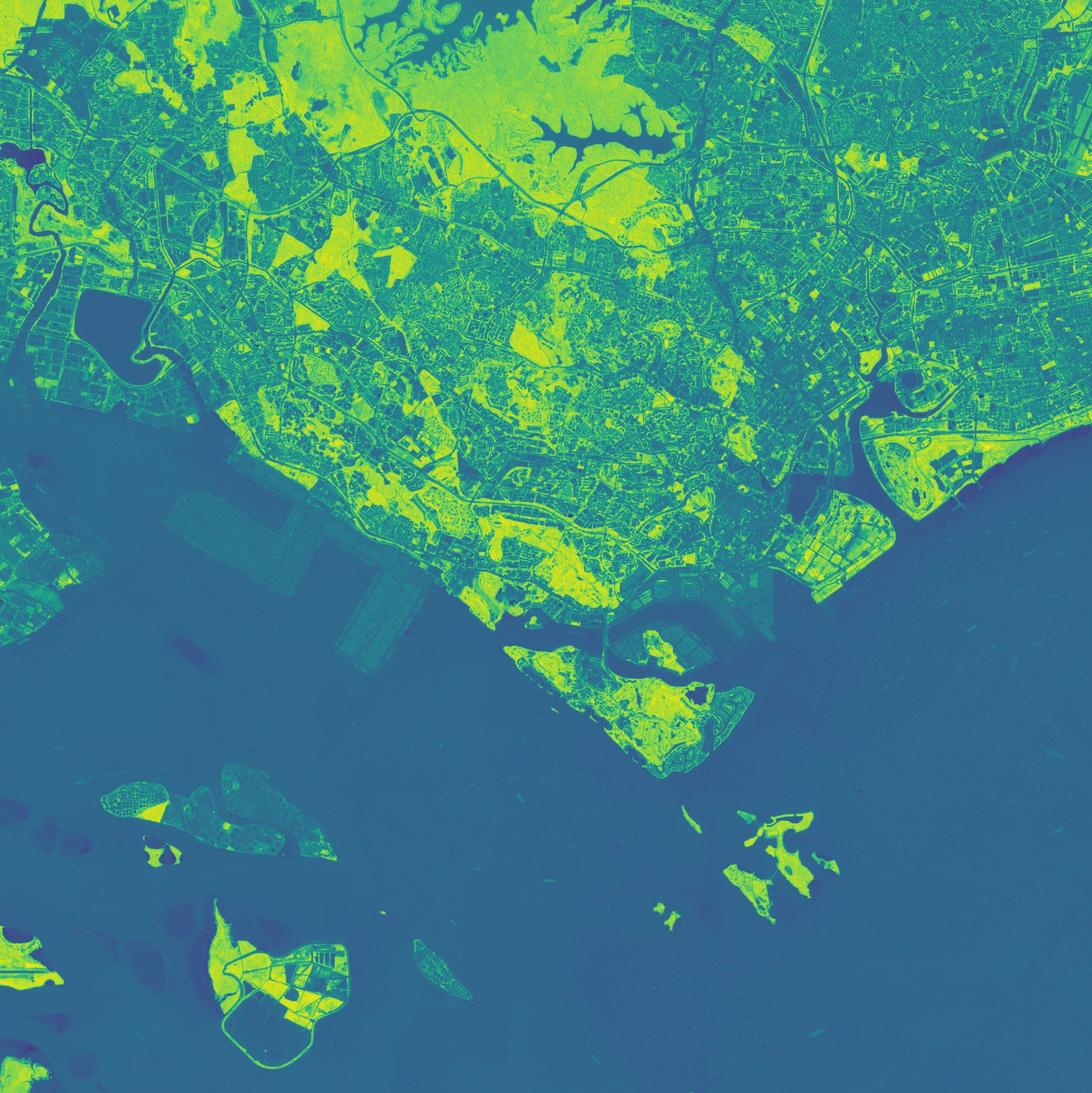
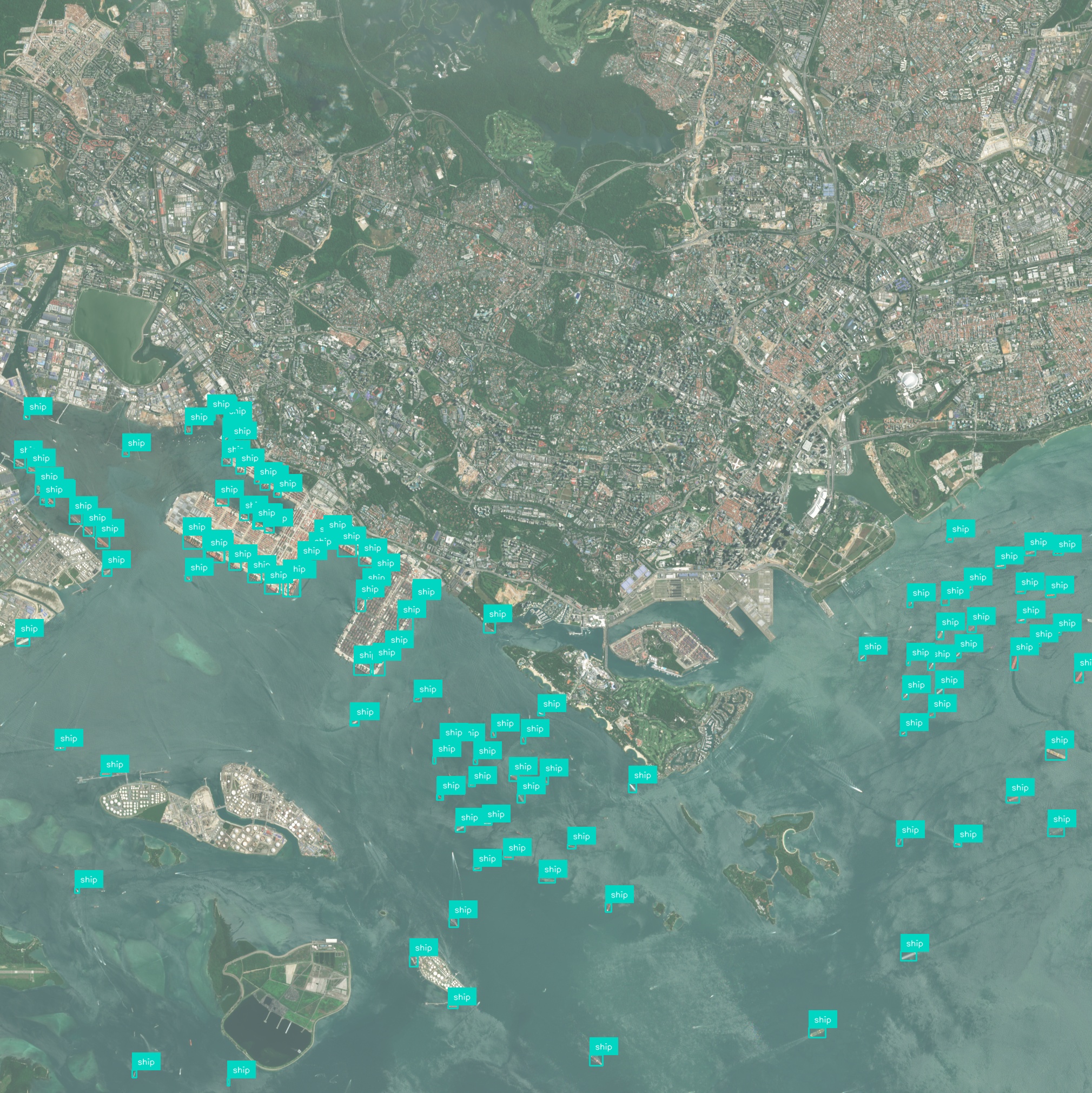




InSAR-derived deformation maps detect millimeter-scale ground movements over time, enabling proactive landslide risk assessment and early warning for vulnerable slopes.





How does it work?
Traditional ground surveys lack the spatial coverage and revisit frequency to capture subtle precursory movements on unstable slopes. InSAR monitoring provides high-resolution, frequent, and wide-area deformation measurements, offering reliable early warning signals to inform risk mitigation.
InSAR generates deformation maps at sub-kilometer grid spacing, capturing localized movement patterns. This granularity enables pinpointing of unstable zones before they reach critical thresholds.
InSAR detects ground shifts down to millimeter scale, revealing subtle precursors to slope failure. This sensitivity supports timely interventions and targeted monitoring efforts.
Satellite constellations deliver regular acquisition cycles, enabling near-real-time tracking of deformation trends. Frequent updates help identify acceleration in ground movement before failure occurs.
InSAR covers broad regions in a single acquisition, allowing simultaneous assessment of multiple sites. This scalability supports regional risk management and prioritization of monitoring resources.
Archived SAR data enable retrospective analysis of long-term deformation patterns. These insights inform stability models and help differentiate seasonal shifts from progressive loading.
Combining InSAR-derived deformation with rainfall, geology, and infrastructure data yields comprehensive risk maps. This integration enhances decision-making for mitigation strategies and emergency planning.
Have a different question and can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Reach out to our support team by sending us an email and we’ll get back to you as soon as we can.
Geospatial AI Platform

AI & foundation models
Deep-learning and foundation models turn raw imagery into ready-to-use insights, so you ship answers instead of training pipelines.

Conversational workflow
Ask questions in plain language and the platform responds with charts, visualizations, and next step suggestions.

GPU-accelerated cloud
Cloud-native architecture spins up on-demand GPU clusters that scale from a single scene to global archives—no manual ops, no bottlenecks.

Any sensor, any format
Optical, SAR, drone, IoT, vector or raster—ingest, fuse, and analyze without conversion headaches.

Insight you can see
Real-time 2D / 3D maps and export-ready plots make results clear for engineers, execs, and clients alike.
Turn satellite, drone, and sensor data into clear, real-time insights using powerful AI – no complex setup, just answers you can see and act on.